There is no specific treatment for fatty liver. Fatty liver can sometimes improve without treatment, but it’s important to get medical advice about the possible risks. The treatment of NAFLD also depends on whether or not you have significant scarring (fibrosis) of your liver.
If you’re diagnosed with NAFLD or nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), your doctor may recommend losing weight, exercising more and following a healthy diet that limits fat and alcohol intake. These lifestyle changes are usually recommended even in people who continue to drink alcohol, because it’s believed that fatty liver disease can become worse when excess weight causes too much stress on the liver.
There are also medical treatments for NAFLD. Your doctor may prescribe weight-loss medication, antioxidants to protect liver cells from damage or medicines that help stop the progression of fibrosis. While there are studies showing the benefits of some supplements and vitamins in treating NAFLD and NASH, there isn’t enough evidence to draw any conclusions about their effectiveness.
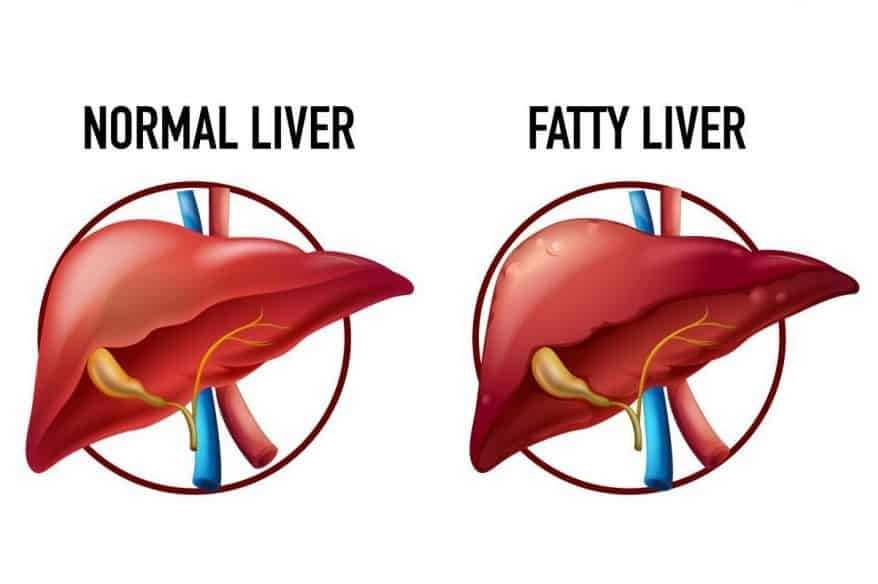
Fatty Liver is generally not serious and usually does not cause any symptoms until it has progressed significantly. Fatty Liver disease can be treated by making changes in your diet and lifestyle as well as taking medications such as erythromycin. Fatty Liver is a common form of chronic liver disease worldwide, including the United States.
Fatty Liver Disease affects approximately 11% percent of the population over age 20 and is a major cause of chronic liver disease in the United States. Fatty Liver Disease is an early stage of Fatty Liver Disease or NAFLD, which occurs when too much fat builds up in cells of your liver.
In Fatty Liver Disease, there’s usually no scarring present on the liver and Fatty Liver Disease often resolves with lifestyle changes such as weight loss, eating a healthier diet and increasing physical activity. Fatty Liver Disease develops over years without causing any symptoms until Fatty Liver Disease has advanced significantly.
Fatty Liver can affect people who drink excessive amounts of alcohol but it also affects people without any drinking history.